MONOX
What is it?
Carbon monoxide is a toxic gas that you can neither see nor smell. It is mainly released by malfunctioning appliances or combustion engines, i.e. those using gas, petrol, fuel oil, coal, wood or ethanol. The majority of poisoning cases occur at home.
Carbon monoxide poisoning affects everyone: headaches, nausea, dizziness and vomiting can all be signs of the presence of carbon monoxide in your home.
Dangers and symptoms
Once inhaled, carbon monoxide is dangerous for health. Once breathed in, carbon monoxide replaces oxygen in the bloodstream. The effects can be fast: in the most severe cases, it can lead to coma or even death in a matter of minutes. Every year, carbon monoxide affects more than one thousand homes in France, causing around one hundred deaths. Those poisoned sometimes suffer lifelong after-effects.
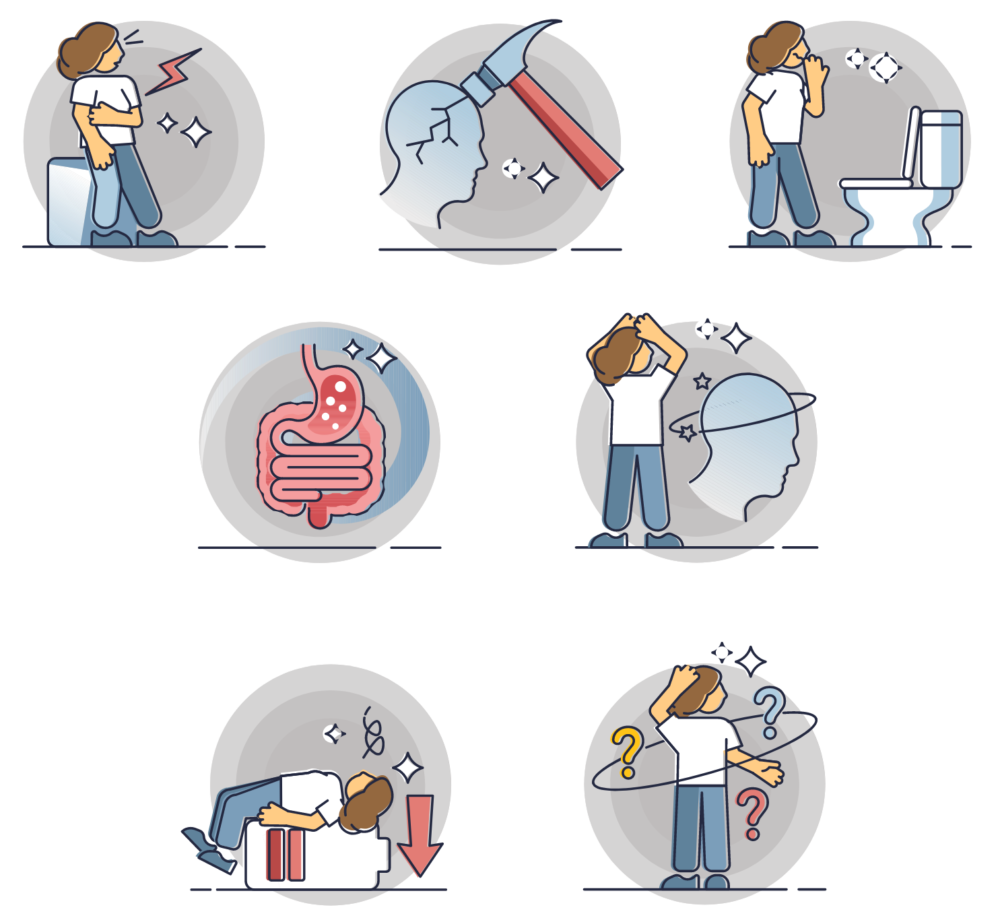
Main symptoms
MILD POISONING
Headaches, nausea, dizziness, drowsiness, concentration deficit, vomiting and coordination disorder.
MODERATE OR SEVERE POISONING
Impaired judgement, confusion, loss of consciousness, convulsions, chest pain, shortness of breath, low blood pressure and coma. Most poisoned victims are no longer able to move and must be rescued. Symptoms appearing in the same place, at the same time of day or week, are highly suggestive of carbon monoxide poisoning.
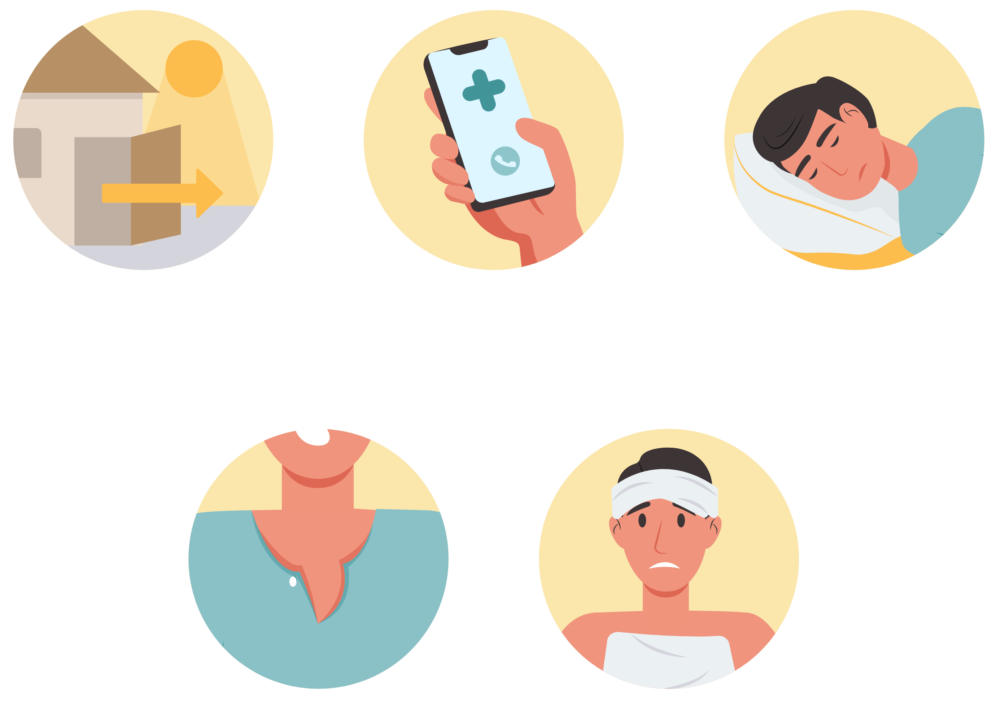

Poisoning: what to do?
- Ventilate the premises immediately by opening doors and windows.
- Switch off your combustion appliances if possible.
- Evacuate the premises and clear all occupants.
- Call emergency services:
 |  | ||
| Single European emergency number | Fire brigade |
- Do not return to the premises until a qualified professional has been called to identify the cause of the poisoning and recommend the necessary corrective action.
How can you protect yourself?
Test your skills :
Expert in preventing carbon monoxide poisoning? Click on the link below to participate in the quiz and evaluate your preparation for the prevention of risks of carbon monoxide poisoning!